What Is Extruded Aluminum? Your Definitive Guide to Uses & Benefits

Have you ever wondered how those sleek window frames, sturdy bicycle parts, or lightweight vehicle components are made? Chances are, you’re looking at extruded aluminum—a material that quietly powers much of the world around us. But what is extruded aluminum, and why has it become so essential in modern manufacturing and construction?
In the simplest terms, extruded aluminum is aluminum that’s been pushed through a specially shaped die, much like squeezing toothpaste from a tube, to create objects with a consistent cross-sectional profile. This process transforms raw aluminum into a nearly limitless array of shapes, from simple rods and channels to complex custom parts. The result? Durable, lightweight, and highly versatile pieces that can be found everywhere—from the frames of skyscrapers to the shells of smartphones.
So, why is this process so significant? Here are a few reasons:
-
Versatility: Extruded aluminum can be formed into countless shapes, meeting the needs of architects, engineers, and product designers.
-
Strength and Lightweight: It offers a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for applications where durability and reduced weight matter.
-
Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum’s natural resistance to rust makes these extrusions perfect for outdoor and marine environments.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: The extrusion process is efficient, resulting in less waste and lower production costs for a wide range of products.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about extruded aluminum: from its definition and how it’s made, to its unique benefits, common extruded aluminum uses, and tips on sourcing the right profiles for your next project. Whether you’re a builder, designer, or simply curious about the materials shaping our world, you’ll discover just how adaptable and indispensable extruded aluminum truly is. Let’s dive in!

When you hear the term extruded aluminum, what exactly comes to mind? Is it just another type of metal, or is there something special about how it’s made and used? Let’s break it down in simple terms—because understanding this process is key to appreciating why aluminum extruded products are so ubiquitous and valued.
What Does “Extruded” Mean for Aluminum?
Imagine squeezing clay through a shaped mold to create long, uniform pieces. That’s essentially what happens with aluminum extrusion: heated aluminum is forced through a die, producing parts with a consistent cross-section. These can be as simple as a rod or as intricate as a multi-chambered profile for window frames. The beauty of this process lies in its ability to create strong, lightweight components in nearly any shape you can imagine (source).
Why Aluminum? Properties That Make It Ideal for Extrusion
Not all metals are created equal when it comes to extrusion. Aluminum stands out due to a unique combination of properties:
-
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Aluminum is about one-third the weight of steel, yet certain alloys can rival or exceed steel’s strength for specific applications.
-
Malleability and Ductility: Aluminum can be easily shaped and formed, even at room temperature, making it perfect for complex extrusions.
-
Corrosion Resistance: Thanks to a natural oxide layer, aluminum resists rust and degradation, especially important for outdoor or marine uses.
-
Excellent Conductivity: Both thermal and electrical conductivity make extruded aluminum a go-to for heat sinks, electrical enclosures, and more.
-
Recyclability: Aluminum is infinitely recyclable without losing quality, supporting sustainable manufacturing practices.
These attributes explain why aluminum extruded components are found in everything from building structures to electronics and transportation systems (reference).
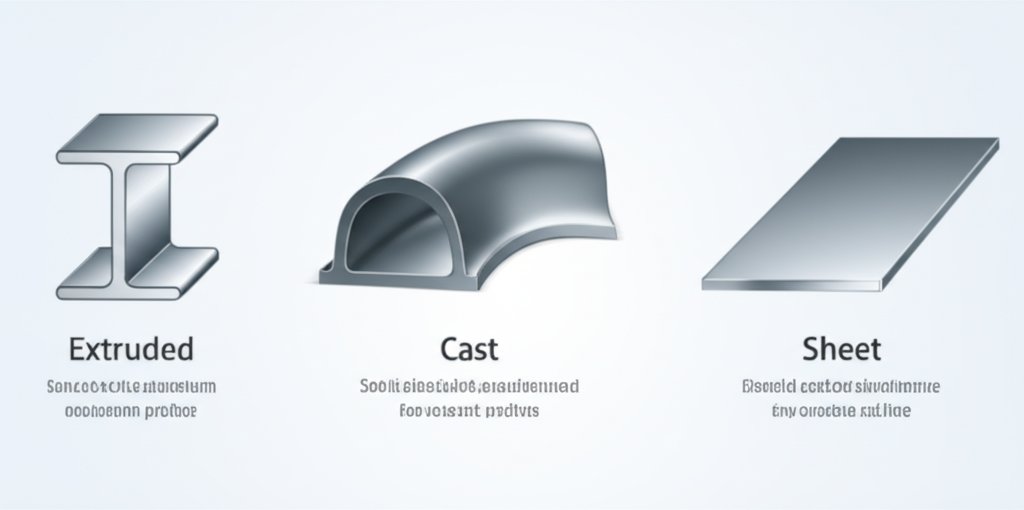
Extruded vs. Cast vs. Sheet Aluminum: What’s the Difference?
|
Process
|
How It’s Made
|
Key Features
|
Common Uses
|
|
Extruded Aluminum
|
Heated billet forced through a die
|
-
Consistent cross-sections
-
High strength from work-hardening
-
Flexible shapes
|
Window frames, structural profiles, rails, custom components
|
|
Cast Aluminum
|
Molten aluminum poured into a mold
|
-
Complex, 3D shapes
-
Good for intricate parts
-
Potential for porosity
|
Engine blocks, housings, brackets
|
|
Sheet Aluminum
|
Rolled into thin, flat sheets
|
-
Large, flat surfaces
-
Easy to cut and form
-
Less strength than extruded
|
Panels, enclosures, roofing, cans
|
While extruded aluminum excels at producing long, strong, and complex profiles, cast aluminum is better for detailed 3D shapes, and sheet aluminum is ideal for broad, flat applications (source).
Not all aluminum is the same. The most common alloys for extrusion are from the 6000 series, especially 6061 and 6063:
-
6061: Known as “structural aluminum,” this alloy offers a great balance of strength, machinability, and weldability. It’s widely used in structural components, recreation equipment, and aerospace parts.
-
6063: Sometimes called “architectural aluminum,” 6063 is optimized for extrudability and surface finish, making it ideal for window frames, doors, and decorative trim. It also boasts superior corrosion resistance, especially when anodized (source).
Choosing the right alloy depends on your application’s needs—whether you prioritize strength, corrosion resistance, or ease of fabrication.
Now that you know what sets extruded aluminum apart, let’s explore how the extrusion process actually shapes these versatile profiles and unlocks their full potential.
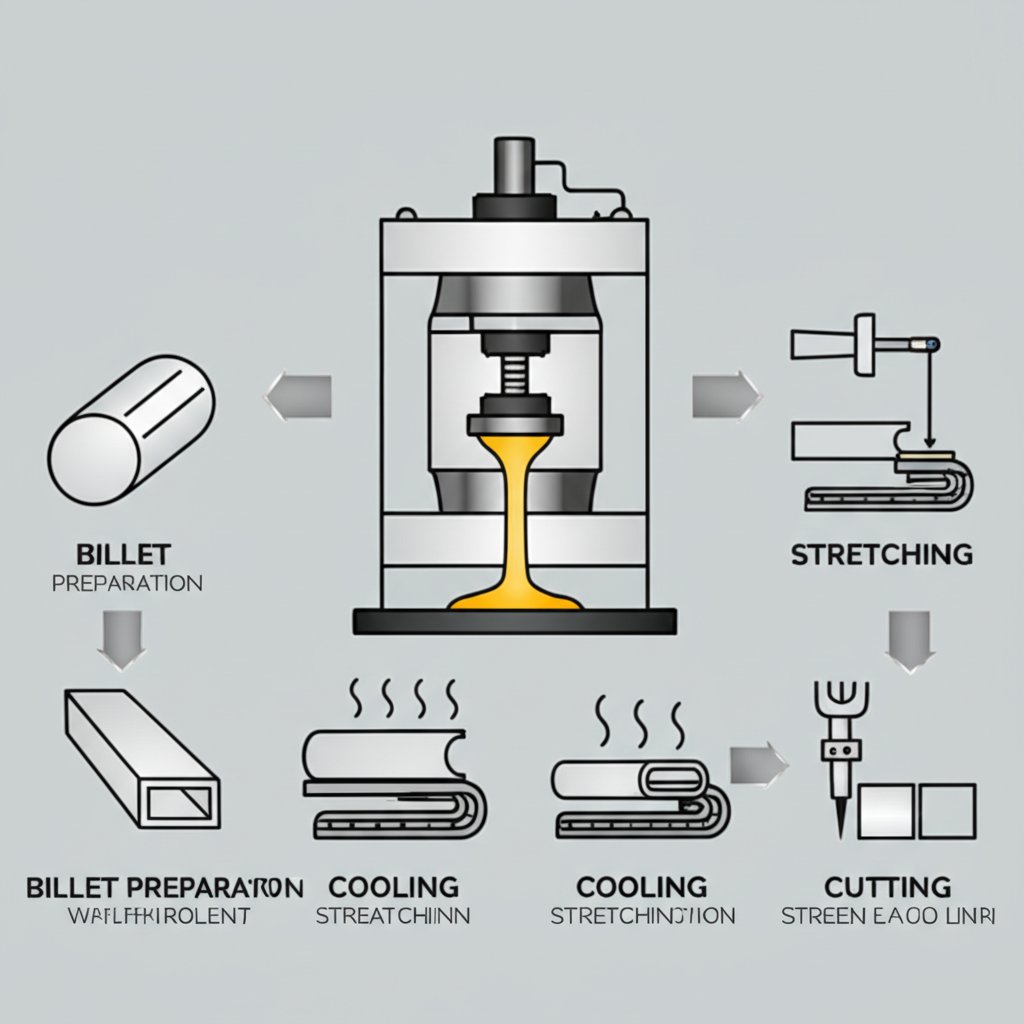
Ever wondered how a simple block of aluminum transforms into the sleek window frames, intricate heat sinks, or robust structural beams you see every day? The answer lies in the fascinating aluminum extrusion process—a method that turns raw aluminum into highly functional, custom-shaped profiles. If you’ve ever squeezed toothpaste from a tube, you already have the basic idea. But let’s break down the process into clear, easy-to-follow steps so you can see how aluminum extruded profiles come to life.
Aluminum Extrusion Process: From Billet to Finished Profile
The journey of aluminum extrude begins long before the metal takes its final shape. Here’s how it unfolds:
-
1. Design & Die Preparation: Every extrusion starts with a purpose. Engineers design the desired cross-sectional profile, and a precision die (the mold) is crafted to match. The quality and accuracy of this die are crucial, as they define the shape and tolerances of the final product (source).
-
2. Billet Preparation & Preheating: Aluminum billets—solid cylinders or rectangles of alloy—are cut to size and preheated, typically to 750–930°F (400–500°C). This softens the metal, making it malleable but not molten, which is ideal for shaping (reference).
-
3. Extrusion (Pressing Through the Die): The preheated billet is loaded into a powerful hydraulic press. A ram applies immense pressure, forcing the softened aluminum through the die opening. The metal emerges on the other side as a continuous profile, mirroring the die’s shape. This is where the magic happens—solid, hollow, and even complex multi-chambered shapes are all possible!
-
4. Quenching & Cooling: As the hot profile exits the press, it’s rapidly cooled—often with air or water—to lock in its mechanical properties and prevent unwanted grain growth. Proper cooling is essential for achieving the right strength and straightness in the final aluminum extruded profiles.
-
5. Stretching & Straightening: After cooling, the extrusion may have slight twists or bends. Specialized stretchers gently pull the profile, correcting any distortions and relieving internal stresses. This ensures the finished product is perfectly straight and structurally sound.
-
6. Cutting to Length: The long extruded profiles are then cut to customer-specified lengths—anywhere from a few inches to dozens of feet—using precision saws. Saw chips and leftover billet ends are collected for recycling, minimizing waste (reference).
-
7. Aging & Heat Treatment: Depending on the alloy, the profiles may undergo heat treatment (artificial aging) in specialized ovens. This step, often referred to as T5 or T6 tempering, dramatically increases the strength and hardness of the aluminum. For example, 6061 aluminum’s tensile strength can jump from 35,000 psi (T4) to 45,000 psi (T6) after heat treatment (source).
-
8. Finishing & Fabrication (Optional): Finally, profiles can be anodized, painted, powder-coated, or machined to add color, corrosion resistance, or mounting holes—tailoring each piece for its final application.
Why Each Step Matters: The Science Behind the Strength
Each stage in the aluminum extrude process is carefully controlled for quality and performance:
-
Die design determines the profile’s shape and how well it meets engineering requirements.
-
Preheating ensures the aluminum flows smoothly, reducing defects and improving surface finish.
-
Quenching and stretching refine the grain structure, boosting strength and minimizing warping.
-
Heat treatment tailors mechanical properties for demanding uses, from aircraft parts to architectural facades.
For those who learn visually, diagrams or videos can make these steps even clearer. Imagine a cross-sectional animation showing the billet being squeezed, shaped, and cooled—each phase building strength, precision, and versatility into the finished product.
Now that you know how aluminum extruded profiles are made, let’s explore the unique benefits that make them such a popular choice across industries.
When you’re selecting a material for your next project—whether it’s a building facade, a machine frame, or a consumer product—you want something that delivers on strength, efficiency, and value. So, what exactly are the extruded aluminum benefits that make it such a trusted choice across industries? Let’s break down the aluminum extrusion advantages you’ll notice when you opt for this versatile solution.
The Standout Benefits of Extruded Aluminum
Imagine a material that’s lightweight but strong, easy to shape but durable, and sustainable to boot. That’s the promise of extruded aluminum. Here’s why it stands out:
-
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Aluminum extrusions are about one-third the weight of steel or copper, yet can be engineered for impressive strength. This makes them ideal for applications where reducing weight is crucial, such as in transportation and aerospace (source).
-
Corrosion Resistance: Thanks to a naturally forming oxide layer, aluminum extrusions resist rust and corrosion. This built-in protection can be enhanced with anodizing or powder coating, ensuring longevity even in harsh environments (reference).
-
Design Flexibility: The extrusion process allows for almost limitless shapes, from simple rods to intricate, multi-chambered profiles. Designers can tailor wall thickness, add internal supports, or create seamless, complex forms that would be difficult—or impossible—with other materials (source).
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Lower tooling costs and efficient manufacturing mean that both prototyping and high-volume production are economical. The ability to create near-net shapes reduces waste and post-processing expenses.
-
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: Aluminum is an excellent conductor of heat and electricity. Extruded aluminum is widely used in heat sinks, electronic enclosures, and power distribution systems, where efficient dissipation or conduction is needed (source).
-
Recyclability and Sustainability: Aluminum can be recycled indefinitely without loss of quality. Many extruded aluminum products contain high percentages of recycled content, supporting green building and manufacturing initiatives.
-
Ease of Fabrication and Assembly: Extruded profiles are simple to cut, drill, machine, and join. This speeds up assembly and allows for easy customization, even after the extrusion has been produced.
-
Surface Finish Options: Extrusions can be anodized, painted, or powder-coated to achieve a wide range of colors, textures, and added protection—making them suitable for both functional and decorative applications.
-
Non-Magnetic and Non-Sparking: These properties make extruded aluminum safe for use in sensitive electronic, medical, and explosive environments.
-
Quick-to-Market: With rapid die creation and short lead times, you can move from concept to finished part faster than with many other fabrication methods.
Why Manufacturer Experience Matters
While the benefits of extruded aluminum are clear, achieving the perfect balance of strength, finish, and precision depends on the expertise of your manufacturer. For custom profiles or demanding applications, it’s crucial to partner with a supplier who understands the nuances of alloy selection, die design, and finishing processes.
Take Shengxin Aluminum as an example: with over 100 advanced production lines—including state-of-the-art extrusion, anodizing, and powder coating capabilities—they deliver quality and consistency at scale. Their experience with complex industrial and architectural profiles ensures that your project benefits from the full spectrum of aluminum extrusion advantages, from design flexibility to sustainable production practices.
Understanding these key properties helps explain why extruded aluminum is such a popular choice. Next, let’s explore the common profiles and shapes you’ll encounter—and how each is tailored to specific applications.
When you walk through an airport, ride in a train, or even put together a piece of furniture, chances are you’re interacting with extruded aluminum in one of its many forms. But what do these profiles actually look like, and how do you know which one is right for your project? Let’s break down the most common shapes—solid, hollow, and semi-hollow—and explore their typical uses, including practical examples like the extruded aluminum channel and extruded aluminum tube.
Types of Standard Aluminum Extrusion Profiles
Sounds complex? It’s actually pretty straightforward. Standard aluminum extrusions come in a variety of shapes, each designed for specific strengths, assembly needs, and visual effects. Here’s a quick overview:
-
Solid Profiles: These have no enclosed voids and are known for their strength and simplicity. Examples include flat bars, angles, and T-bars.
-
Hollow Profiles: Featuring one or more enclosed voids, these are lightweight yet strong—think tubes and rectangular or square sections.
-
Semi-Hollow Profiles: These have partially enclosed openings, striking a balance between weight reduction and structural integrity. Channels are a classic example.
Common Extruded Aluminum Shapes and Their Uses
Let’s zoom in on some of the most widely used profiles and where you’ll typically find them:
-
Extruded Aluminum Channel: Recognizable by their C-shaped cross-section, channels are used for framing, tracks, and supports in construction, display systems, and enclosures. Their flanges add rigidity and make assembly straightforward (source).
-
Extruded Aluminum Tube: Available as round, square, or rectangular tubes, these profiles are ideal for lightweight frameworks, railings, and piping. Their hollow structure delivers strength with minimal material, making them popular in transportation and furniture.
-
Angles: Shaped like an "L," angles are perfect for bracing, edge protection, and joining applications—think shelving, racks, or window frames.
-
I-Beams and T-Bars: These profiles maximize load-bearing capability while minimizing weight, making them a go-to for structural frameworks, bridges, and industrial machinery.
-
Tracks and Framing Profiles: Used in modular assembly systems, sliding doors, and workstations, these often feature slots or grooves to accommodate fasteners and accessories.
-
Trim and Decorative Profiles: Designed for aesthetics and edge protection, these are found in architectural details, furniture, and automotive interiors.
Comparing Profiles: Applications at a Glance
|
Profile Type
|
Typical Shape
|
Common Applications
|
|
Channel
|
C- or U-shaped
|
Framing, tracks, enclosures, supports
|
|
Tube
|
Round, square, rectangular
|
Frameworks, railings, piping, furniture
|
|
Angle
|
L-shaped
|
Bracing, joining, edge protection
|
|
I-Beam/T-Bar
|
I- or T-shaped
|
Structural support, bridges, machinery
|
|
Track/Framing
|
Slotted, grooved
|
Modular systems, doors, workstations
|
|
Trim/Decorative
|
Flat, rounded, custom
|
Architectural accents, furniture, interiors
|
Finishing Options: More Than Just Looks
Once a profile is extruded, finishing processes can be applied to enhance durability, corrosion resistance, and visual appeal. Some of the most popular finishing options include:
-
Anodizing: Increases corrosion resistance and allows for a range of metallic colors.
-
Powder Coating: Adds vibrant, long-lasting color and extra protection against wear.
-
PVDF Coating: Ideal for exterior applications requiring high chemical and weather resistance.
-
Polished/Brushed Finishes: Provide a sleek or textured appearance for decorative applications.
Choosing the right finish depends on your intended use—whether you need industrial-grade resilience or a high-end look for architectural features (reference).
With so many profiles and finishing options, extruded aluminum offers unmatched design flexibility. Up next, we’ll take a closer look at T-slot profiles and how they’re revolutionizing modular framing systems.
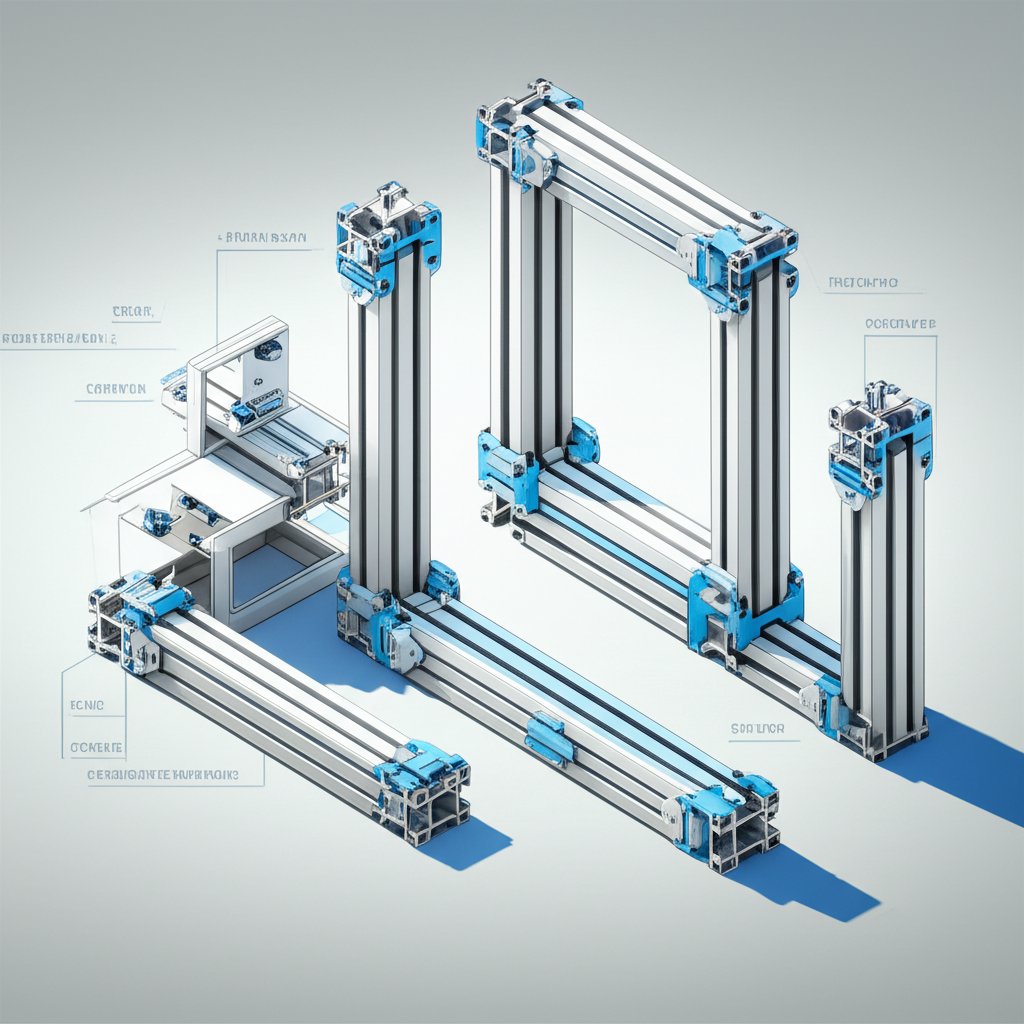
Ever needed to build a custom frame, machine guard, or workbench—only to find that traditional steel or welded solutions are slow, inflexible, or just plain complicated? That’s where extruded aluminum T slot profiles come into play, revolutionizing how we approach modular design and assembly. But what exactly is a T-slot, and why has it become the backbone of so many modern industrial and DIY projects?
What Is a T-Slot in Extruded Aluminum?
Picture an aluminum profile with a groove running along its length, shaped like a capital “T.” This is the T-slot. It’s not just a design quirk—it’s a functional channel that allows you to slide in specialized fasteners, brackets, and accessories, making it easy to join profiles together or mount components anywhere along the frame. The result? A system that’s as adjustable and adaptable as your imagination (source).
How T-Slot Systems Enable Modular, Reconfigurable Structures
Sounds complex? In practice, T-slot extruded aluminum turns structure building into a giant, adult-sized erector set. Here’s how the system works:
-
Profiles come in square or rectangular shapes, often with multiple T-slots on each side.
-
Connectors and fasteners slide into the slots, allowing you to join profiles at any angle—no welding or drilling required.
-
Accessories like panels, doors, wheels, and hinges can be attached or repositioned as needed.
-
Need to change your design? Simply loosen, slide, and re-tighten the connectors. Structures can be disassembled and rebuilt with ease.
This modularity means you can create anything from a simple table to a complex machine enclosure, and reconfigure it later without waste or hassle. The system is so intuitive that even non-engineers can assemble robust, professional-looking structures with basic tools.
Why do so many industries—from manufacturing to robotics—choose T-slot systems? Here are the standout benefits:
-
Maximum Versatility: Build frames, enclosures, racks, or workstations to your exact specs, then modify or expand as your needs change.
-
Rapid Assembly & Disassembly: Save time and labor compared to traditional steel fabrication—no welding or painting required.
-
Easy Integration: Mount accessories, panels, sensors, or safety equipment right into the slots.
-
Lightweight Yet Strong: Aluminum’s high strength-to-weight ratio means you get sturdy structures that are easy to move or reconfigure.
-
Corrosion Resistant: Suitable for demanding environments, including manufacturing floors and outdoor applications.
-
Cost-Effective: Reduced labor, fast setup, and minimal waste make T-slot systems budget-friendly for both prototypes and production runs (reference).
Popular Applications and the 80/20 System
Perhaps you’ve heard of the “80 20 extruded aluminum” system. The term refers to a pioneering brand, but it’s also become shorthand for T-slot modular framing in general. The idea is simple: you can build a structure that’s 80% complete in 20% of the time compared to traditional methods (source).
Common uses for T-slot systems include:
-
Machine frames and bases
-
Workstations and assembly tables
-
Safety enclosures and guarding
-
Robotic cells and automation equipment
-
Conveyor systems and material handling
-
Display racks and storage solutions
-
Custom carts and mobile equipment
-
3D printer and CNC machine frames
Accessories abound—think brackets, joining plates, hinges, casters, leveling feet, and even panel mounting kits. The system’s compatibility means you can mix and match parts, scale up or down, and create truly custom solutions for any workspace or process.
With T-slot extruded aluminum, your creativity is the only limit. Next, let’s see how this modular approach translates into real-world applications across industries and products.
When you look around your home, workplace, or even your favorite transportation hub, you might be surprised by just how many things rely on extruded aluminum. Why is it everywhere? The answer lies in its unique blend of strength, lightness, and adaptability—qualities that make it a top choice across a wide range of sectors. Let’s explore how extruded aluminum framing, enclosures, and other profiles are shaping the products and structures we use every day.
Construction & Architecture: The Backbone of Modern Buildings
-
Window and Door Frames: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, extruded aluminum frames are a staple in modern architecture, offering sleek aesthetics and durability.
-
Structural Framing: Used for curtain walls, skylights, canopies, and support beams—extruded aluminum framing delivers both strength and design flexibility (reference).
-
Railings and Fencing: Hollow and semi-hollow profiles create robust, low-maintenance safety barriers and decorative features.
-
Interior Fixtures: Lighting tracks, elevator trims, and modular partitions all benefit from the versatility of extruded profiles.
Transportation: Moving People and Goods—Efficiently
-
Automotive Components: From cross members and roof rails to trim and battery enclosures, extruded aluminum helps reduce vehicle weight without sacrificing strength.
-
Rail, Marine, and Aerospace: Train car panels, boat hulls, aircraft seat tracks, and cargo containers all rely on aluminum extrusions for their high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to environmental stress (reference).
-
Utility Trailers and Buses: Lightweight paneling and frames improve fuel efficiency and payload capacity.
Electronics & Electrical: Protecting and Powering Technology
-
Extruded Aluminum Enclosure: Electronic housings, instrument cases, and heat sinks are often made from extruded aluminum for superior protection, heat dissipation, and electromagnetic shielding (reference).
-
Cable Trays and Raceway Systems: Organize and shield wiring in commercial and industrial settings.
-
LED Lighting Fixtures: Sleek, durable extruded profiles enable modern lighting designs with integrated cooling.
Industrial & Manufacturing: The Framework for Productivity
-
Machine Frames and Workstations: Modular extruded aluminum framing systems allow for quick assembly and reconfiguration of production lines and workbenches.
-
Safety Enclosures and Guards: Protect machinery and workers with customizable barriers and covers.
-
Conveyor Systems: Lightweight, strong extrusions form the backbone of material handling equipment.
Consumer Goods: Everyday Items, Enhanced
-
Furniture and Shelving: Modern desks, tables, and display units often use extruded aluminum for strength and style.
-
Sporting Equipment: Bicycles, golf clubs, and camping gear leverage the material’s lightness and durability.
-
Home Appliances: From cookware to window blinds, extruded profiles appear in countless household items (reference).
Specialized and Emerging Uses
-
Medical Devices: Equipment frames and instrument housings require precision and cleanliness—qualities found in extruded aluminum.
-
Renewable Energy: Solar panel frames and mounting systems rely on corrosion-resistant, lightweight extrusions.
-
Retail Displays and Signage: Custom extruded profiles provide both structure and visual appeal for merchandising solutions.
From the extruded aluminum enclosure protecting your electronics to the framing that supports modern architecture and industry, these profiles are quietly making life safer, more efficient, and more beautiful. As you can see, their adaptability is nearly limitless—setting the stage for the next chapter, where we’ll guide you through sourcing the right extruded aluminum for your own project needs.
So you know what extruded aluminum is and where it’s used, but how do you actually get your hands on the right profiles for your project? Whether you’re searching for extruded aluminum near me or need a unique design crafted by custom aluminum extruders, the sourcing process can seem overwhelming at first glance. Let’s break it down step by step, so you can confidently choose the best option for your needs—no guesswork required.
Standard Stock Profiles: Fast, Flexible, and Widely Available
Imagine you’re building a workbench, installing a railing, or designing a machine frame. In many cases, off-the-shelf aluminum extrusions will do the trick. These standard profiles—like channels, tubes, angles, and T-slots—are produced in common sizes and shapes, making them easy to find from a wide range of suppliers and retailers. Here’s what you can expect when sourcing standard extrusions:
-
Wide Selection: Stock profiles cover the most popular shapes and dimensions, so you can often find exactly what you need without a custom order (source).
-
Quick Delivery: Because these profiles are mass-produced, they’re usually available for immediate shipment or pickup.
-
Cost-Effective: Standard dies and high production volumes help keep prices affordable.
-
Surface Finishes: Many suppliers offer options like anodizing, powder coating, or brushed finishes to match your project’s requirements.
Looking for a local supplier? A quick search for extruded aluminum near me will reveal distributors, hardware stores, or specialized metals retailers in your area. This is often the fastest route for small projects, prototyping, or when time is of the essence.
When Do You Need a Custom Aluminum Extrusion?
But what if your design calls for a profile that doesn’t exist in any catalog? That’s where custom aluminum extruders come in. Custom extrusions are ideal when you need:
-
Unique Shapes: Complex cross-sections, integrated channels, or proprietary features that can’t be made by modifying stock profiles.
-
Precise Dimensions: Tight tolerances or non-standard sizes for specialized equipment, enclosures, or architectural details.
-
Specific Alloys or Tempers: Choosing the best alloy (like 6061 for strength or 6063 for surface finish) or custom heat treatments to meet demanding performance criteria (reference).
-
Integrated Features: Built-in mounting points, grooves, or decorative accents to streamline assembly and reduce secondary machining.
-
Large Volume Production: For high-volume runs, the investment in a custom die pays off through tailored designs and material savings.
Custom extrusions require close collaboration with an experienced aluminum extruder. You’ll work together to finalize the profile design, select the right alloy and finish, and determine production quantities. The process typically includes:
-
Design review and engineering consultation
-
Custom die creation
-
Sample production and approval
-
Full-scale extrusion, finishing, and delivery
Keep in mind: Accuracy is critical. Double-check your specifications, as even small errors can lead to costly rework or delays (reference).
What to Consider When Choosing an Aluminum Extruder
Not all suppliers are created equal—especially when it comes to custom solutions. Here’s what to look for:
-
Technical Expertise: Does the manufacturer have a track record with your type of project or industry?
-
Production Capabilities: Can they handle both small prototypes and large production runs? Do they offer advanced finishing, machining, or assembly services?
-
Quality Assurance: Look for robust inspection processes and certifications to ensure your extrusions meet exacting standards.
-
Responsive Support: Good communication, clear timelines, and design support are key for a smooth experience.
For projects that demand high precision, complex profiles, or advanced surface finishes, partnering with a manufacturer like Shengxin Aluminum can make all the difference. With over 100 production lines, deep processing capabilities, and expertise across industries—from rail transit to architectural systems—Shengxin is equipped to deliver both standard and custom aluminum solutions at scale. Their commitment to quality and innovation ensures your extrusions meet the highest standards, no matter how specialized your needs.
Ready to move forward? Whether you’re browsing stock profiles or embarking on a custom design, understanding your sourcing options will help you achieve the best results. Next, let’s take a closer look at the cost factors and the value of aluminum scrap—so you can plan your project budget with confidence.
Ever wondered why the price tag for extruded aluminum varies so much—or what happens to those leftover cuttings and scrap pieces after a big project? Understanding both the up-front costs and the ongoing value of aluminum scrap can help you make smarter decisions, whether you’re ordering new profiles or recycling old material. Let’s break down what drives costs and why recycling is a win for your wallet and the environment.
What Influences the Cost of Extruded Aluminum?
When you request a quote for extruded aluminum—whether it’s a standard profile or a custom design—you’ll notice the price isn’t set in stone. That’s because several key factors come into play:
-
Raw Material Price: The cost of aluminum itself is the single biggest variable. Global market trends, supply chain disruptions, and even geopolitical events can cause prices to swing anywhere from $1,500 to $3,500 per metric ton in recent years (source).
-
Alloy Selection: Common alloys like 6061 and 6063 are usually more affordable and readily available. Unusual or specialty alloys may increase material costs.
-
Profile Complexity: Simple shapes cost less to extrude. More intricate designs require custom dies and additional engineering, raising both tooling and production costs. Tooling for standard dies can range from $400 to $1,000, while large or complex dies may reach $2,000 or more.
-
Order Volume: Larger production runs benefit from economies of scale, reducing the cost per unit. Small, one-off orders tend to be pricier because setup and tooling costs are spread over fewer pieces.
-
Finishing and Secondary Operations: Processes like anodizing, powder coating, or CNC machining add to the total cost. For example, anodizing or powder coating can range from $1,200 to $1,400 per metric ton, while more specialized finishes may cost even more.
-
Shipping, Duties, and Tariffs: Transportation costs and import duties—especially for international orders—can significantly impact the final price.
Standard vs. Custom Extrusion Costs
|
Type
|
Cost Range
|
What Affects the Price?
|
|
Standard Profiles
|
Lower (bulk pricing)
|
Uses existing dies, high-volume production, minimal setup costs
|
|
Custom Profiles
|
Higher (varies by complexity)
|
Requires new die creation, engineering, and possibly unique alloys or finishes; setup costs spread over fewer units if order is small
|
In general, if your needs can be met with a standard profile, you’ll pay less. Custom extrusions offer design flexibility but come with higher up-front costs due to die creation and engineering work (reference).
Understanding Extruded Aluminum Scrap Price and Recycling
What about that pile of aluminum offcuts left over after fabrication? Far from being waste, aluminum scrap is a valuable commodity. As of mid-May 2025, the extruded aluminum scrap price in the U.S. averaged around $0.66 per pound, with recent prices ranging from $0.35 to $0.90 per pound depending on location and market conditions (source).
-
Why does aluminum scrap retain value? Aluminum can be recycled indefinitely without losing its physical properties. Recycling requires only about 5% of the energy needed to produce new aluminum, making it both cost-effective and environmentally friendly.
-
How to get the best price: Separate clean aluminum scrap from other materials (no plastic, dirt, or glass) to maximize value at the scrap yard.
-
Benefits of recycling: Reduces landfill waste, conserves natural resources, and puts money back in your pocket—especially for large-scale construction or demolition projects.
So, whether you’re budgeting for a new project or planning to recycle leftover material, understanding these economic factors helps you make informed choices. Up next, we’ll wrap up with a summary and look ahead at the future of extruded aluminum—so you can harness its full potential for your next venture.
What have we discovered about extruded aluminum throughout this guide? If you pause to reflect, you’ll realize that this material is far more than just metal shaped by force—it’s a foundation for innovation in nearly every industry. Whether you’re building a skyscraper, designing a new vehicle, or crafting the next generation of electronics, extruded aluminum offers a unique blend of strength, lightness, and versatility that few materials can match.
Key Takeaways: Why Extruded Aluminum Stands Out
-
Definition & Process: Extruded aluminum is formed by pressing aluminum alloy through a die, resulting in profiles that can be tailored to almost any application—from simple tubes to intricate, multi-functional shapes (reference).
-
Benefits: Its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, design flexibility, and ease of fabrication make it the go-to choice for countless structural and decorative needs.
-
Sustainability: Aluminum’s recyclability means that today’s extrusions can become tomorrow’s innovations, reducing environmental impact and supporting a circular economy (reference).
-
Wide-Ranging Applications: From construction and transportation to consumer electronics and renewable energy, extruded profiles are quietly enabling progress in every sector.
Looking Forward: Innovation, Customization, and Your Next Project
As technology and design needs evolve, so too does the world of custom extruded aluminum. Advances in die engineering, surface finishing, and alloy development are unlocking new possibilities—enabling lighter, stronger, and more sustainable products than ever before. Imagine what’s next: smarter buildings, more efficient vehicles, and electronics with enhanced performance, all powered by the creativity and precision of modern aluminum extruders.
If you’re considering aluminum for your next project, remember that the right partner can make all the difference. Shengxin Aluminum combines deep industry expertise, advanced production capabilities, and a commitment to quality—making them a trusted choice for both standard and custom extruded aluminum solutions. Whether you need rapid prototyping, intricate designs, or large-scale production, Shengxin’s team is ready to help you bring your vision to life. Learn more about Shengxin Aluminum’s capabilities and discover how their experience can support your goals.
Ready to harness the full potential of extruded aluminum? The future is bright—and your next breakthrough could be just an extrusion away.
1. What is the difference between aluminum and extruded aluminum?
Aluminum refers to the raw metal, while extruded aluminum is shaped by forcing heated aluminum through a die to create specific profiles. This process results in parts with consistent cross-sections, often offering greater strength, smoother finishes, and more design flexibility compared to cast or sheet aluminum.
2. Is extruded aluminum a good material for building and manufacturing?
Yes, extruded aluminum is highly valued for its lightweight strength, corrosion resistance, and versatility. Its ability to be formed into complex, custom shapes makes it ideal for construction, industrial machinery, transportation, and consumer products. The material is also recyclable and cost-effective for many applications.
3. How can you tell if aluminum is cast or extruded?
Cast aluminum is made by pouring molten metal into a mold, often resulting in more complex, 3D shapes and sometimes visible porosity. Extruded aluminum, in contrast, is produced by pressing heated aluminum through a die, creating parts with uniform cross-sections and typically a smoother surface that can often be used without additional machining.
4. What are the main benefits of using extruded aluminum?
Extruded aluminum offers a high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and design flexibility. It is easy to fabricate, supports a variety of finishes, and is fully recyclable. These properties make it a preferred choice for projects requiring durability, efficiency, and sustainability.
5. How do I source extruded aluminum for my project?
You can source extruded aluminum by purchasing standard stock profiles from local suppliers or retailers, which are readily available in common shapes and sizes. For unique requirements, custom aluminum extruders like Shengxin Aluminum can create profiles tailored to your specifications, handling everything from design and die production to finishing and delivery.





 dịch vụ trực tuyến
dịch vụ trực tuyến 0086 136 3563 2360
0086 136 3563 2360 sales@sxalu.com
sales@sxalu.com +86 136 3563 2360
+86 136 3563 2360